Classifiers are important components in many computer vision tasks, serving as the foundational backbone of a wide variety of models employed across diverse applications. However, understanding the decision-making process of classifiers remains a significant challenge. We propose DiffEx, a novel method that leverages the capabilities of text-to-image diffusion models to explain classifier decisions. Unlike traditional GAN-based explainability models, which are limited to simple, single-concept analyses and typically require training a new model for each classifier, our approach can explain classifiers that focus on single concepts (such as faces or animals) as well as those that handle complex scenes involving multiple concepts. DiffEx employs vision-language models to create a hierarchical list of semantics, allowing users to identify not only the overarching semantic influences on classifiers (e.g. the 'beard' semantic in a facial classifier) but also their sub-types, such as 'goatee' or 'Balbo' beard. Our experiments demonstrate that DiffEx is able to cover a significantly broader spectrum of semantics compared to its GAN counterparts, providing a hierarchical tool that delivers a more detailed and fine-grained understanding of classifier decisions.
-1.png)
Our pipeline processes a set of sample domain-specific images and a text prompt using a VLM to generate a hierarchical semantic corpus of attributes relevant to a specific domain. Based on this corpus, DiffEx identifies and ranks the most influential features affecting the classifier's decisions, sorting them from most to least impactful (rightmost image). The hierarchical explanation of semantics (such as beard and its subtypes) provides a fine-grained understanding of which features drive classifier outputs.
(1)-1.png)
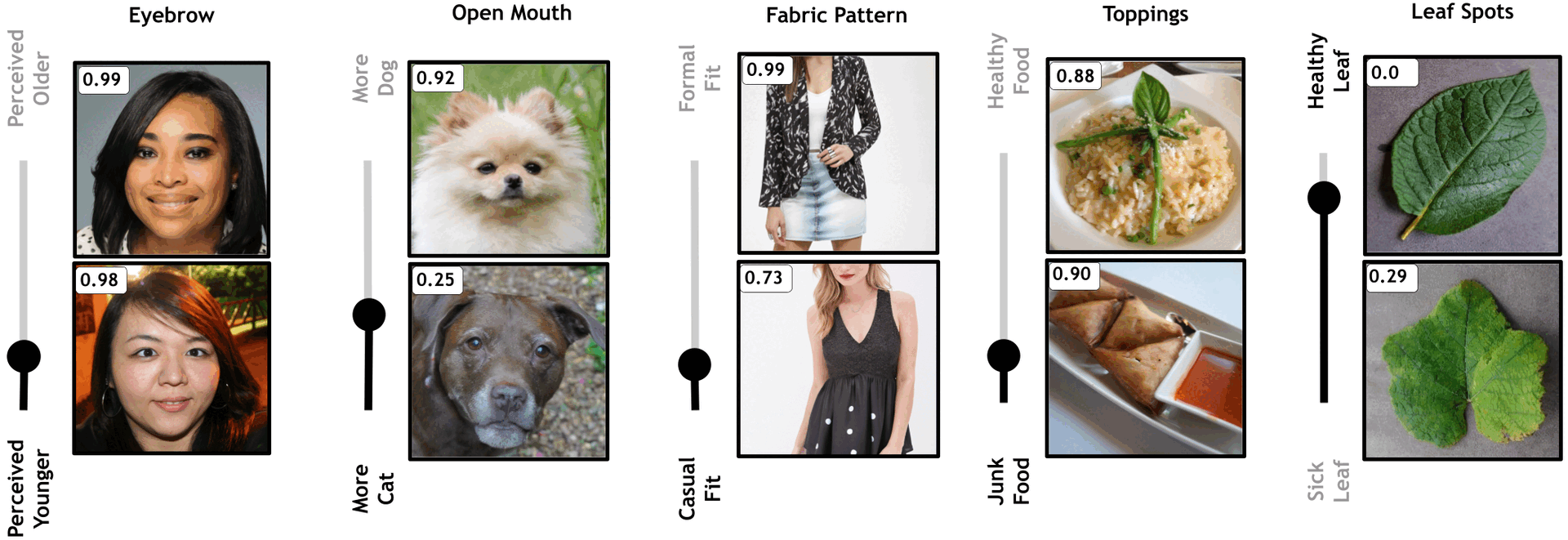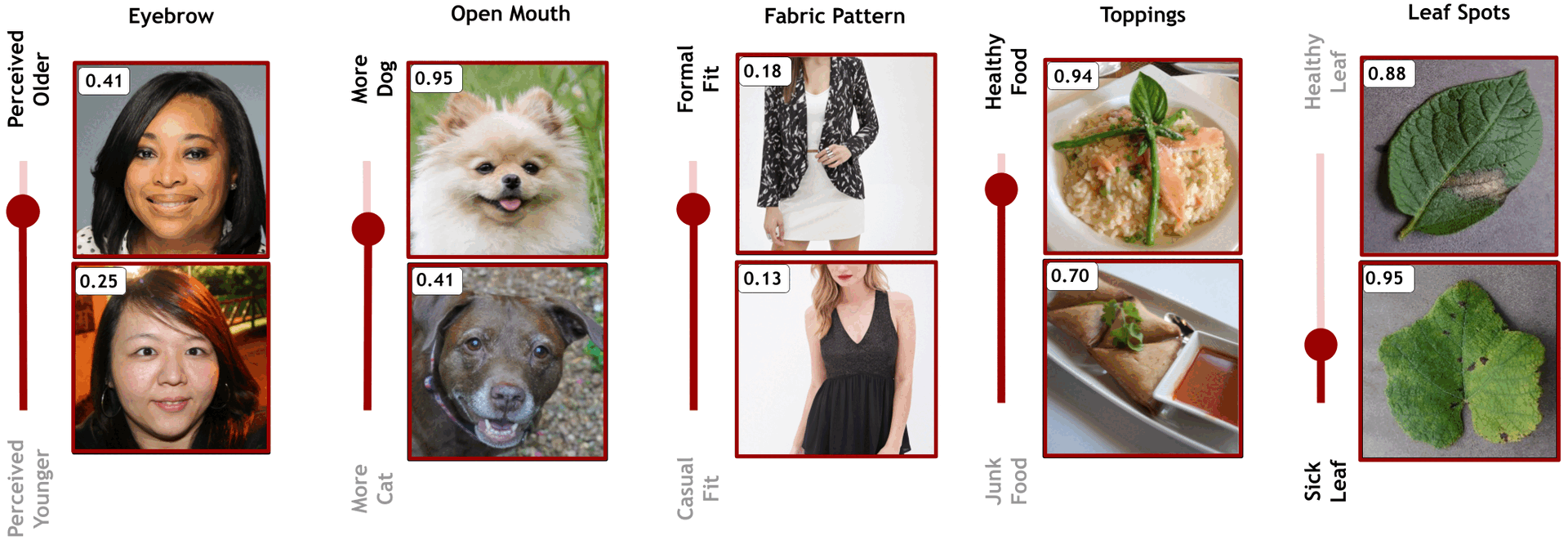
Top-7 Discovered Facial Attributes for the Age Classifier Our method effectively identifies key attributes and their top hierarchical subtypes for a perceived age classifier in the facial domain, using our proposed classifier-based search algorithm. For each attribute, the edited images and their respective subtypes are displayed in a hierarchical structure, outlined with a black border. The score for the young label is shown in the top-left corner of each image.
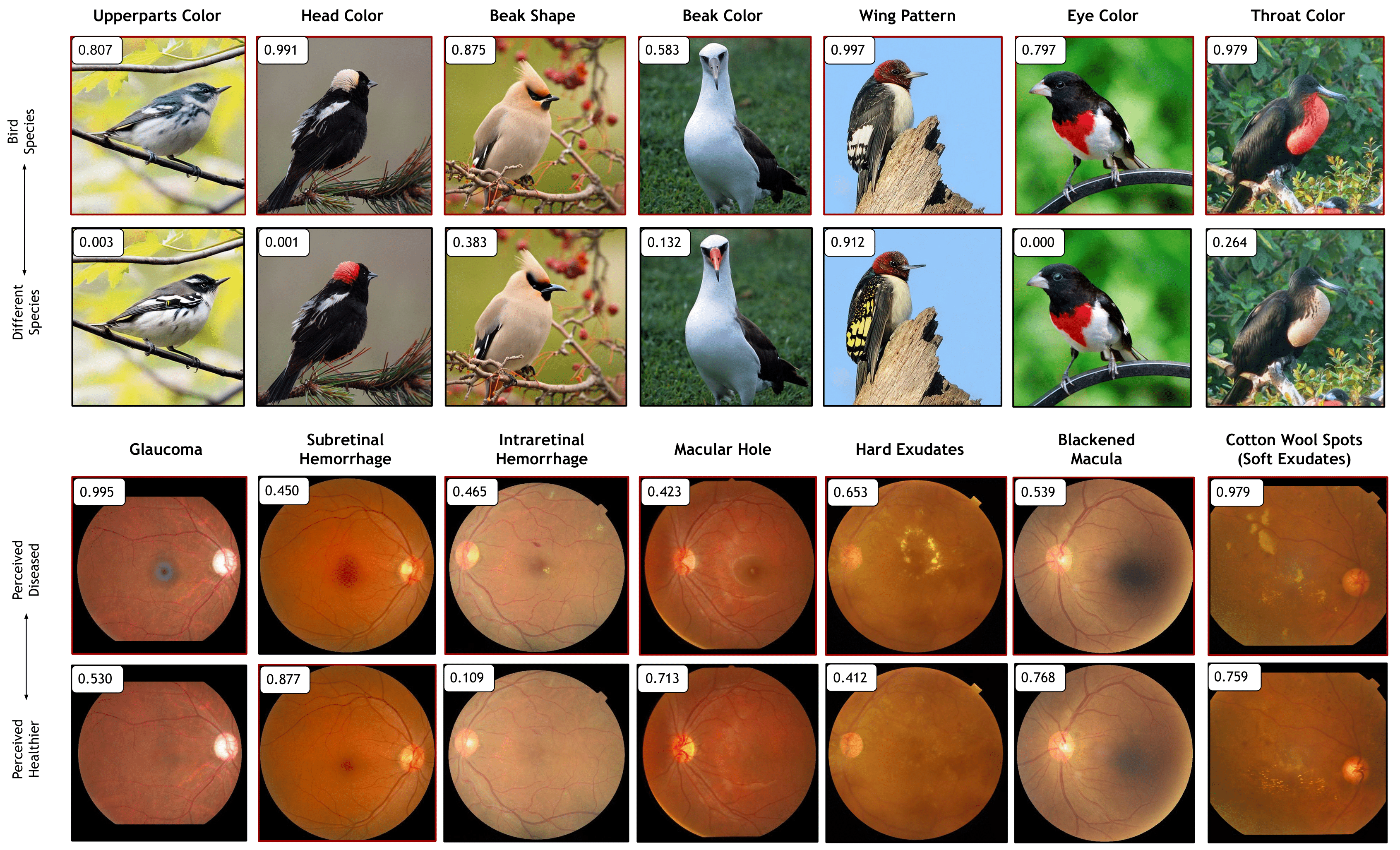
DiffEx successfully discovered top attributes relevant to bird species and retinal diseases.
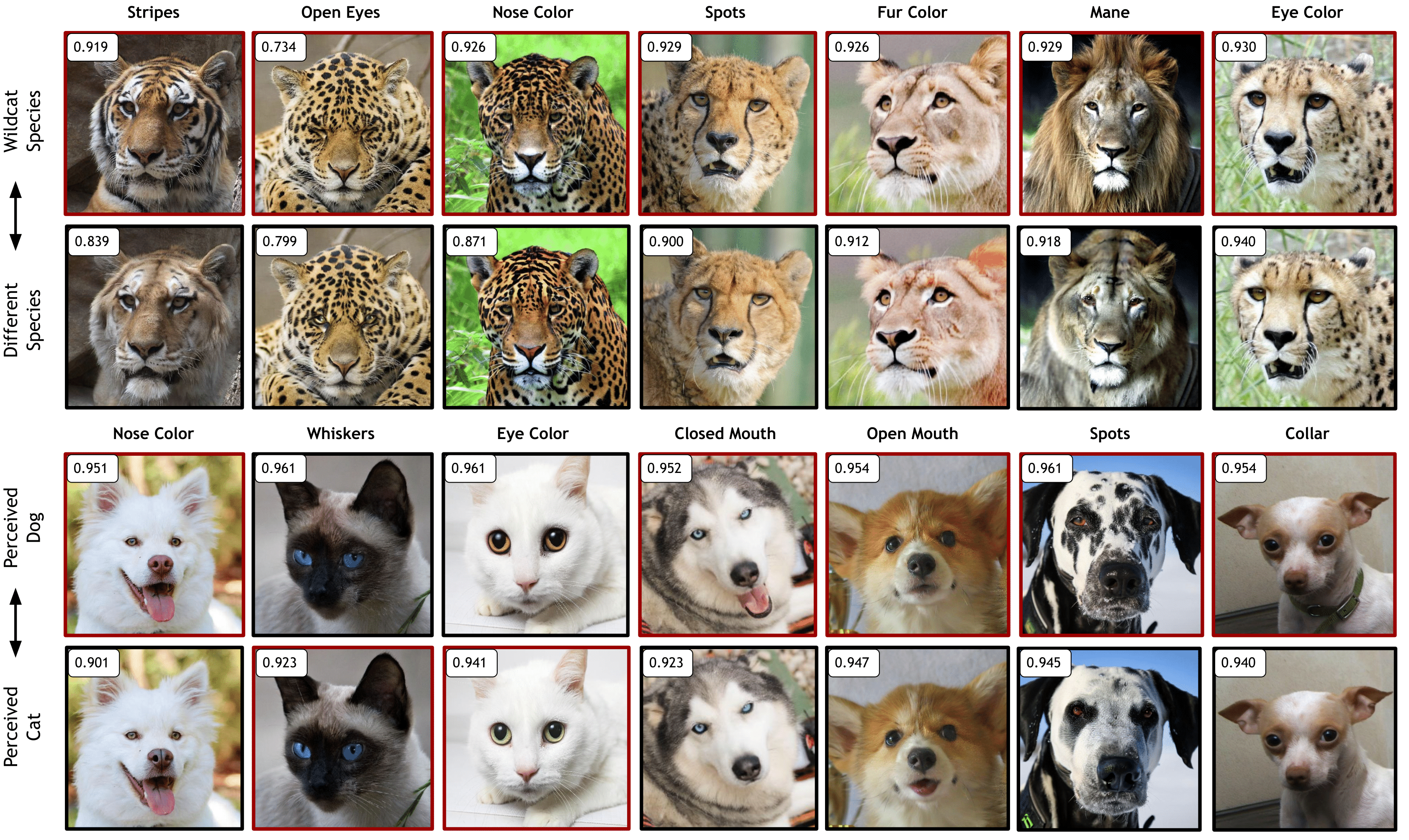
DiffEx can be seamlessly applied to diverse domains, effectively extracting and ranking meaningful attributes relevant to specific classifiers. The figure illustrates how DiffEx identifies the most impactful features across various novel domains, providing insights into the key attributes influencing classifier decisions.
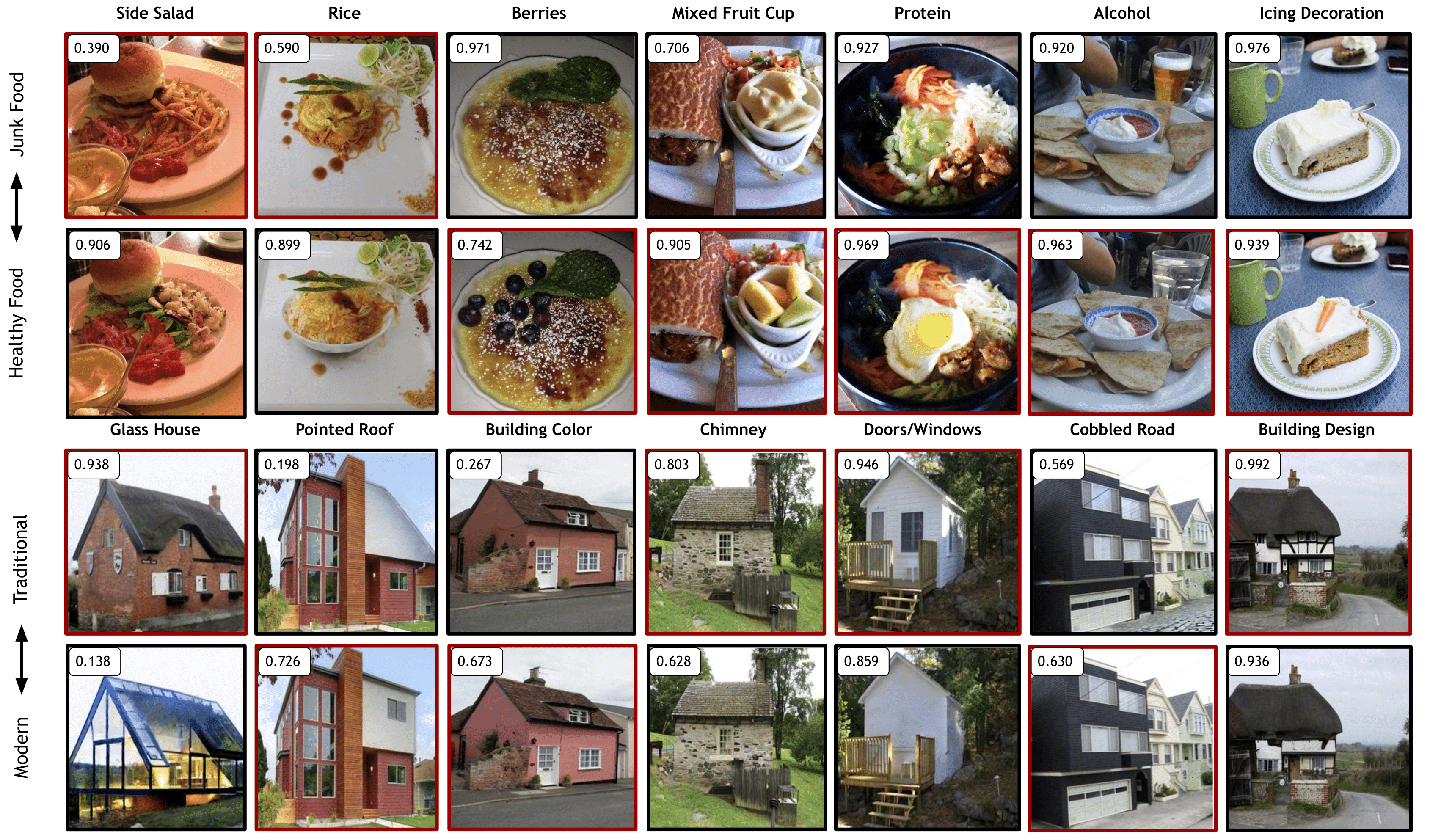
DiffEx showcases the ability to identify more significant features across diverse domains compared to existing methods.
@article{kazimi2024explaining,
title={Explaining in Diffusion: Explaining a Classifier Through Hierarchical Semantics with Text-to-Image Diffusion Models},
author={Kazimi, Tahira and Allada, Ritika and Yanardag, Pinar},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.18604},
year={2024}
}